Why Is The Left Ventricle Thicker Than The Right?
 Why Is The Left Ventricle Thicker Than The Right
Why Is The Left Ventricle Thicker Than The Right It all began when a friend of mine asked me: "Why is the left ventricle of the heart thicker than the right?". At first, I was a little confused but I soon found out the answer. And I'd love to share it with you.
What Are the Chambers of the Heart?
The heart is divided into two separate sides, which are called the left and right sides. The right side is responsible for receiving oxygen-depleted blood from the body and sending it to the lungs. The left side, on the other hand, is responsible for receiving oxygenated blood from the lungs and sending it back to the body.
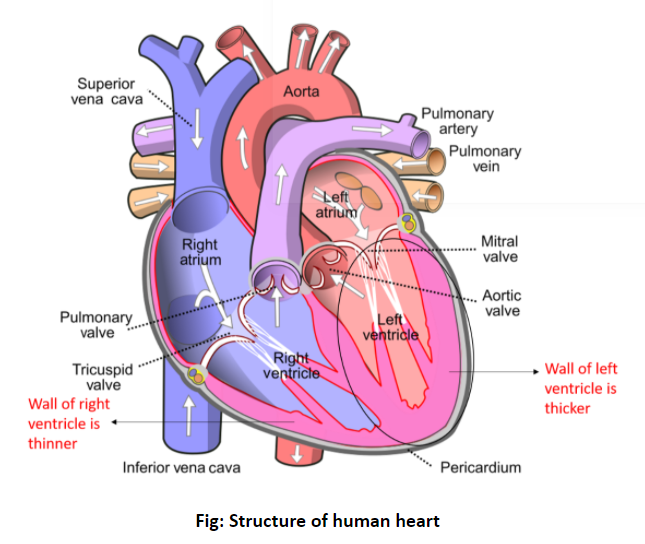
Within these two sides are four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The right atrium and right ventricle make up the right side of the heart, while the left atrium and left ventricle make up the left side.
The two ventricles are the pumping chambers of the heart and have the thickest walls, which is necessary to withstand the pressure of the blood flow.
Why Is the Left Ventricle Thicker?
The left ventricle has the thickest wall of all four chambers because it needs to pump oxygenated blood to the entire body. This requires a much higher blood pressure than the right ventricle, which only pumps oxygen-depleted blood to the lungs. The left ventricle’s thicker wall allows it to better withstand the higher pressure.
In addition, the left ventricle has a larger volume of blood to pump with each stroke than the right ventricle. This means it needs a slightly thicker wall to prevent it from over-stretching. The thicker walls give it the strength to push against the higher pressure and larger volume, allowing it to pump efficiently.
It's worth noting that the thickness of the walls of the ventricles can also vary depending on a person's activity level, age, and overall health. For instance, if a person is exercising regularly, the left ventricle will become thicker due to the higher volume of blood it needs to pump during each stroke.
How Does the Left Ventricle Differ in Structure?
In addition to having a thicker wall than the right ventricle, the left ventricle also varies in structure. It has three valves, two leaflets and an insertable section, which are designed to control the one-way blood flow. The two leaflets form a valve that prevents the backflow of blood and the insertable section helps to reduce the energy required to pump the blood.
The right ventricle, on the other hand, only has two valves, which are designed to prevent backflow of blood. This means that it is not as efficient at controlling the direction of the blood flow as the left ventricle.
What Can We Learn From the Left Ventricle?
The left ventricle is an amazing example of how our body works to keep us healthy. Its thicker wall allows it to withstand higher blood pressure and larger volumes of blood, while its valves help to control the direction of the blood flow. Once we understand the workings of the left ventricle, we can better appreciate the important role it plays in keeping us healthy.
Moreover, the left ventricle is an incredible example of how our bodies can adapt to different levels of activity and stress. Its walls become thicker when we are exercising regularly and this allows it to better cope with the increased amount of blood it needs to pump. This shows us how our body can modify itself to better keep us healthy.
Conclusion
The left ventricle has a thicker wall than the right ventricle for a number of reasons. It prevents it from over-stretching when pumping oxygenated blood around the body, while its valves help to control the direction of the blood flow. By understanding the workings of the left ventricle, we can better appreciate its role and the amazing ways our body adapts to different activity levels.
Post a Comment for "Why Is The Left Ventricle Thicker Than The Right?"